在上一篇文章中,我们完成了 HomeView 的基本布局。接下来我们来编写一下数据层(Model ViewModel)。
大概包括两个方面:数据的获取(JSON URLSession) 和 UI ViewModel 的数据同步。
数据的获取
首先我们使用的 Api 是 Hikotoko。随机获取一条 Hikotoko 的 JSON 如下。
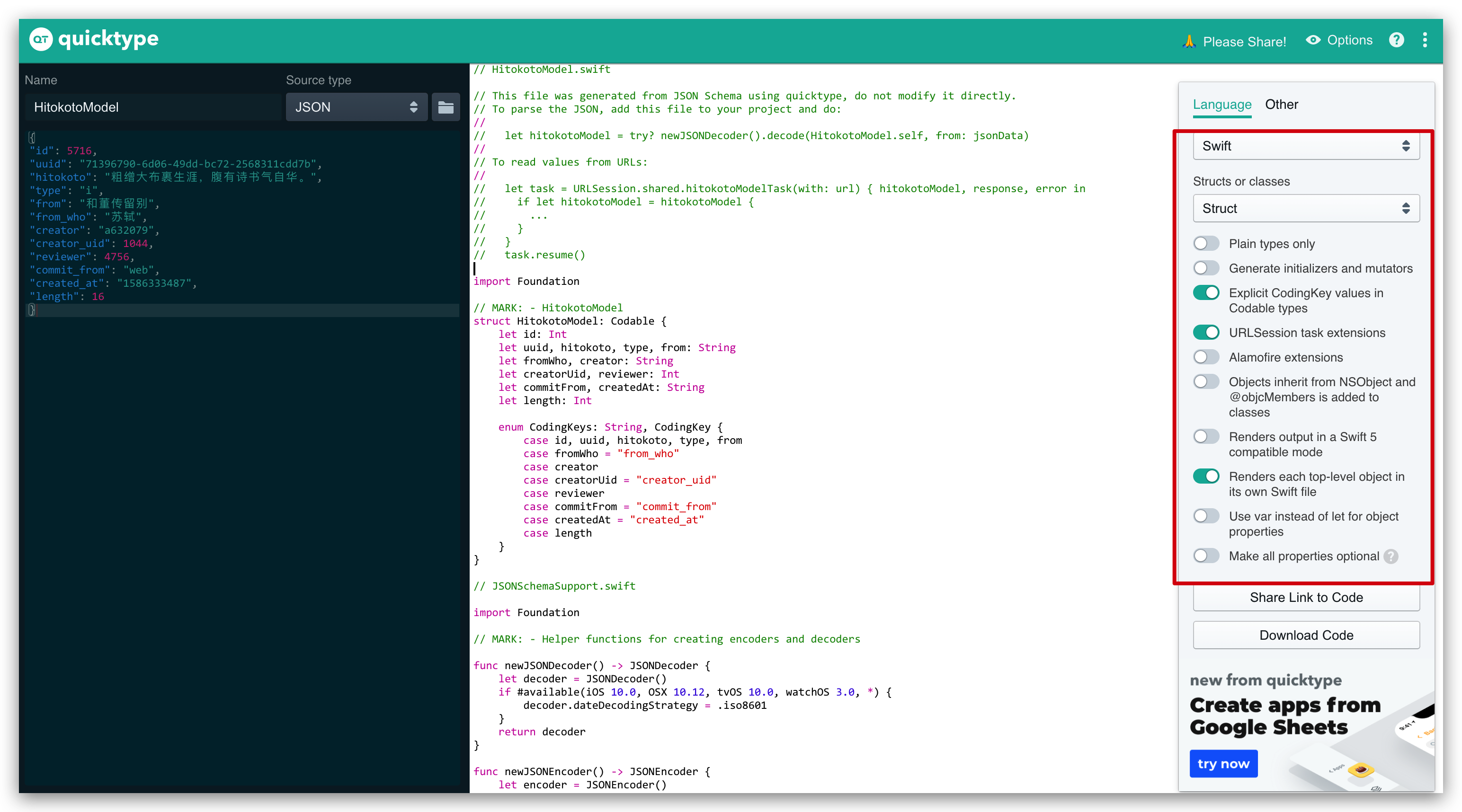
使用工具 JSON2Swift 将 JSON Model 转化为 Swift Struct。工具推荐使用: https://app.quicktype.io/
右侧选项根据需要修改。仅参考。
1609121675559
使用此工具的好处是,他把 URLSession 也自动构建好了。并给出了实例。
新建一个 Swift 文件,命名为 Model.swift 将生成的代码复制到新文件。
再新建一个 Swift 文件,命名为 ViewModel.swift,写入以下代码。
在 HomeView 中调用此方法。修改 HomeView 的代码为

效果已经有了,但是没有加载完成时(受限于网络,弱网),会出现一片空白。如果未加载完成时,显示加载中.. 可能会比较好。
在未加载完成时,model 为 nil ,那么只需要判断是不是 nil 就行了。我本来想用 Group 包裹 if 判断语句实现。理论上是可行的,但是由于 Group 中 if 不支持使用 Stack 包裹。出现如下报错。
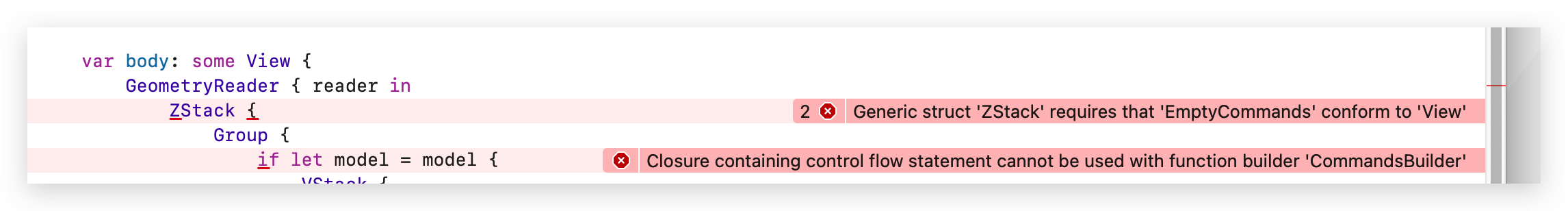
换一种方法。转而使用 @ViewBuilder,首先提取组件。在这个 struct 里新增一个 some View。
然后在 body 的合适地方替换成。
响应式数据流
接下来我们实现保存 Hikotoko 到 喜欢。我们需要用到本地存储和响应式数据流。
本地存储可以使用 UserDefaults,响应式数据流使用 ObservableObject。
新建一个 Swift 文件,命名为 Like.swift
使用 ObservableObject protocol 使得一个对象成为可被观察的,当被装饰 @Published 的属性改变时,会触发 UIView 更新。
在 MeetApp.swift 中挂载 Like 为 environmentObject。增加如下代码。
@main
struct MeetApp: App {
@State var activeTabIndex = 0
+ let like = Like()
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
TabView(selection: $activeTabIndex) {
ContentView().tabItem {
Label("遇见", systemImage: activeTabIndex != 0 ? "circle" : "largecircle.fill.circle")
.onTapGesture {
activeTabIndex = 0
}
}
.tag(0)
LikeView().tabItem {
Label("喜欢", systemImage: activeTabIndex != 1 ? "heart.circle" : "heart.circle.fill")
.onTapGesture {
activeTabIndex = 1
}
}
.tag(1)
}
.accentColor(.pink)
+ .environmentObject(like)
}
}
}
在 HomeView 中,ActionView 中的 Like Button,修改 action 为
在顶部增加
完整如下
装饰了 @EnvironmentObject 的属性会自动获取上层 View 挂载的 environmentObject,不需要层层传递。类似 React 中的 Context。
数据的存储
在 Like.swift 中新建一个 Class,代码如下。
我们使用 refreshStore 方法把 Like 中 likes 数据保存到本地数据中。因为 likes 不是普通的 Array,所以不能直接使用 Userdefaults.set() 的方法写入,否则会 runtime crash。首先使用 PropertyListEncoder 将数据序列化。在此之前,请注意 LikeModel 实现了 Codable Protocol。
同样在 Like init 的时候读取本地保存的数据。当然也需要先反序列化数据。
在修改 likes 后,同时写入到本地数据。可以使用 didSet 计算属性很容易完成。修改 likes 属性为。
之后完整的 Like.swift 如下:
下一篇文章,将构建 LikeView。
(未待完续)